Current Affairs 12 May 2024 Daily GK Updates. Current Affairs 12 May 2024 , 21 May, 12 May 2024, 19 May 15 and of complete Current Affairs of this month.
Current Affairs 12 May 2024 Check Current Affairs 12 May 2024 Complete Explanation and Criticism. Today’s Current Affairs 12 May 2024 is Based More Upon Banking Sector !!
Join Our Facebook Page for Latest Govt Jobs and UPSC Exams Updates
: https://www.facebook.com/examupsc
Looking for More Jobs ? Just Find Best Job Suits you here
: https://www.examsleague.co.in/catagory/jobs
Overview Of Current Affairs 12 May 2024 – GK Updates
What's in this Article ?
- 1 Overview Of Current Affairs 12 May 2024 – GK Updates
- 2 Current Affairs 12 May 2024
- 3 Current Affairs 12 May 2024 – Three Pillars :
- 4 Current Affairs 12 May 2024
- 5 Current Affairs 12 May 2024 : Daily GK Updates – Pillars :
- 6 Current Affairs 12 May 2024 : Daily GK Updates – India :
- 7 D-SIB: Domestic Systemically Important Banks: Too Big to Fail?
| Terms | Explanation | ||||||||||||
| Bank’s capital: | Bank’s own money (apart from Liability + Asset) | ||||||||||||
|
Tier 1 capital: |
Most Liquid Capital with bank
Can be sold easily to ward off Crisis Eg: Common Shares + Preferential Shares |
||||||||||||
|
Tier 2 capital: |
Not as liquid as Tier-I
Eg: Debts (bonds) + Hybrid instruments (Having both characteristics of Debt and Equity) |
||||||||||||
| Tier 3 capital: | Least Liquidity | ||||||||||||
|
Capital adequacy requirements (CAR)
|
Ratio of a Bank’s Capital to its Risk (absorb a reasonable amount of loss)
Higher CAR à More stability Therefore, Basel Capital adequacy requirement (CAR) = 9% of RWA (Risk weighted assets) OR BASEL CAR: [7% of RWA in T1] + [2% of RWA in T2] |
||||||||||||
|
Risk Weighted Assets (RWA) |
Have 9 Crore as TOTAL CAPITAL ADEQUACY if you want to loan out 100 crore |
Current Affairs 12 May 2024
[button color=”” size=”” type=”3d” target=”” link=””] Basel I [/button]
[button color=”” size=”” type=”square_outlined” target=”” link=””]Criticisms:[/button]
- Rigidity of “one-size fits” approach
- Absence of risk sensitivity in estimating capital requirements
[button color=”” size=”” type=”3d” target=”” link=””]Basel II:[/button]
Banks had to maintain the minimum capital requirement of 8% against the risk weighted assets
[button color=”” size=”” type=”square_outlined” target=”” link=””]Computation of RWA based on ‘three’ Risks:[/button]
- Credit,
- Market, and
- Operational Risks
Current Affairs 12 May 2024 – Three Pillars :
- Minimum capital requirements,
- Supervisory review process, and
- Market discipline
[button color=”” size=”” type=”square_outlined” target=”” link=””]Criticisms:[/button]
Failure to address a number of issues during the Financial Crisis (2007–08)
- Pro-Cyclical: In better times, it didn’t impose additional capital requirement on banks but during the crisis, looked out for banks bringing in more of Capital. It was this failure to add in additional capital that led to hurting the financial system, plunging in deep into Recession.
- Absence of Regulation Governing Leverage: The assumption that the risk based capital requirement would in itself mitigate the risks of excessive leverage became a cause of the crisis.
- Did not consider liquidity risk as part of capital regulation and this led on to a Solvency Risk
- More focus on the individual financial institutions, ignoring the risks arising from the interconnectedness across institutions and markets leading the crisis to spread across various financial markets.
Current Affairs 12 May 2024
[button color=”” size=”” type=”3d” target=”” link=””]Basel III:[/button]
[button color=”” size=”” type=”3d” target=”” link=””]A Global Regulatory Framework for more Resilient Banks and Banking systems[/button]
[button color=”” size=”” type=”square_outlined” target=”” link=””]Objectives:[/button]
- To strengthen global capital and liquidity regulations with the goal of promoting a more resilient banking sector
- To improve the banking sector’s ability to absorb shocks arising from financial and economic stress.
[button color=”” size=”” type=”square_outlined” target=”” link=””]Enhancements:[/button]
- Augmentation in the level and quality of capital
- Introduction of liquidity standards
- Modifications in provisioning norms
- Introduction of leverage ratio
Current Affairs 12 May 2024 : Daily GK Updates – Pillars :
- Minimum Regulatory Capital Requirement based on Risk weighted assets
- Maintaining capital (Credit, market and Operational Risk)
- Supervisory Review Process
- Regulatory Tools and Frameworks to deal with risks
- Market Discipline
- Transparency of Banks
Current Affairs 12 May 2024 : Daily GK Updates – India :
- Minimum capital requirement in India is higher at 9% of the risk-weighted assets
- All commercial banks – Regional rural banks
- Commercial banksà approximately 87% of total banking system assets
- Public sector banks: Market share of 73% banking assets and 82% of bank branches
- Foreign banksà 6% of the Indian banking sector
[button color=”” size=”” type=”3d” target=”” link=””]Issues with Indian Banks:[/button]
- Profitability
- Capital acquisition
- Liquidity Needs
- Limits on lending: ‘Urgent need to take control of bad loans (NPAs) + selection of borrowers based on proper due diligence and not on relationships’
- Bank consolidation: ‘Consolidate weaker banks with stronger ones and this would attract more funding from both international and local capital markets’
- Pressure on Yield on Assets
- Pressure on Return on Equity: ‘Will face decline in the short run’
- Stability in the Banking system:
‘The need for banks to ensure that the de-recognised portion of existing additional Tier I and II capital is replaced with Basel III complaint capital leads to the balance sheet not being static and therefore there is a need to step up the capital to address this.’
[button color=”” size=”” type=”square_outlined” target=”” link=””]RoE:[/button]
Return on equity measures a corporation’s profitability by revealing how much profit a company generates with the money shareholders have invested.
Current Affairs 12 May 2024 : India – Current Scenario :
- Budget 2014: Banks themselves will have to raise money by selling shares to public, in a phase manner but Government will continue to remain the majority shareholder.
- India remains “Compliant” with the Basel III global regulatory framework for implementing risk-based capital requirements
- An overarching issue regarding the use of the word “may” in India’s regulatory documents for implementing binding minimum requirements; but RBI has maintained its usage explaining that it is binding on the Banks.
- There still remains distance to be covered in complying with the standards for liquidity coverage ratio (LCR), or highly liquid assets held by banks to meet their short-term obligations.
[button color=”” size=”” type=”square_outlined” target=”” link=””]Criticisms:[/button]
- There exists tools like CRR + SLR + Regular Reporting to RBI as a sufficient “backup” mechanisms to prevent banking crisis in India
- The approach of one-size-fits-all shouldn’t be applied. It restricts the flow of money in the economy of a developing country where it can be provided to those who really need it.
[button color=”” size=”” type=”square_outlined” target=”” link=””]Connecting the Dots:[/button]
- Examine how the Basel-III mechanism plans to correct the wrongs done by Basel-II?
- Is India capable enough to prevent a banking crisis? Critically analyse the issues faced by the Banking sector w.r.t the Basel-III norms.
D-SIB: Domestic Systemically Important Banks: Too Big to Fail?
Current Affairs 12 May 2024 : Types of SIB’s
[button color=”” size=”” type=”3d” target=”” link=””]Global Systematically Important Bank (G-SIB)[/button]
- Too important to fail all over the world
- By BASEL Committee on Banking Supervision
[button color=”” size=”” type=”3d” target=”” link=””]Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIB)[/button]
Country’s Central Bank identifies + decides the parameters to be complied
[button color=”” size=”” type=”3d” target=”” link=””]India’s RBI: A Cautious Beginning[/button]
- ICICI and SBI:
- Combined Assets: Over one-fifth of the country’s GDP
- Strong Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR)
- Risk of operations: Risks emanating from the Quality of Borrowers
- Huge divergence in Size + Nature of Operations
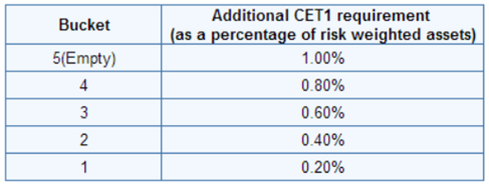
- Capital fixed at a lower point–>0.2 per cent to 0.8 per cent extra capital, based on the category under which they fall
- Indicators used:
- Size: Loans + Savings Deposits, etc
- Interconnectedness: With different Financial Institutions
- Substitutability: Services can be substituted or are replaceable
- Complexity: Higher Complexity–>More Time + Expenses to resolve disputes/issues
- Weak Credit growth + Rising Bad Loan + NPA’s–>Should not over-burden Banks (less number of Bank designated as D-SIB this year)
- Foreign bank in India(Global Systemically Important Bank)
- Branch presence in India
- Need to maintain additional CET1 capital surcharge in India (as applicable on it as G-SIB), proportionate to its Risk Weighted Assets in India
[button color=”” size=”” type=”square_outlined” target=”” link=””]Benefits[/button]
- Stringent Supervision + Strict Regulation of Rules
- Behaviour Management: Efficient Working + No crisis
- Additional Capital: Will act as a Shock Absorber
- Tax-payer’s Money: Proper Utilization in providing services to the taxpayers
[button color=”” size=”” type=”square_outlined” target=”” link=””]Limitations[/button]
- No stringent control over NBFC’s
[button color=”” size=”” type=”square_outlined” target=”” link=””]Why?[/button]
- NBFC’s: In the ‘shadow’ of the main banks
- Carry bank like operations
- But not subject to Regulations
- RBI guidelines but not up-to-the-mark
- FSLRC Report by Justice BN Srikrishna
- Creation of new Single Statutory Bodies for proper Accountability + Supervision
- Inclusion of less number of Banks
- Additional Capital to be maintained is very less; might amount to less strictness and a lethargic mind-set à Bad for the future
- Reforms to revive some PSB’s: Too slow; Leads to leaving out of a huge amount of earnings and the scope of capital that it can raiseà Hasten the process!
[button color=”” size=”” type=”square_outlined” target=”” link=””]Connecting the Dots:[/button]
- What do you mean by Shadow Banks? What are the reforms suggested by Justice BN Srikrishna’s report for Financial Sector Legislative Reforms (FSLRC)?
- Examine the reasons plaguing the revival of some of our PSB’s. Suggest a way ahead.
That’s All For Daily GK Updates Around the World Current Affairs 12 May 2024.
BookMark ” Current Affairs ” to Get Regular Updates on Current Affairs Daily !!!